Acids & Bases Problem Set
Question 10: Relationship between pKa and pH
Tutorial to help answer the questionThe correct operational relationship between pKa and pH is that:
A. both are log functions. B. both are always < 7 for acids, and >7 for bases. C. These two concepts are not operationally related in any way since biological fluids contains mixtures of too many acids and bases. D. When pH = pKa , the compound in question will have a charge of +0.5. E. When pH = pKa , the ionizable compound in question (whether acid or base) will be half protonated and half deprotonated.
Tutorial
pKa and pH| The "operational" relationship between pKa and pH is mathematically
represented by Henderson-Hasselbach equation:
pH = pKa + log [A-] / [HA] One oft-cited solution to this equation is obtained by arbitrarily setting pH = pKa.
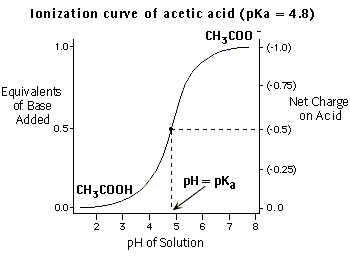
In this case, log([A-] / [HA]) = 0, and [A-] / [HA] = 1. In words, this means that when the pH is equal to the pKa of the acid, there are equal amounts of protonated and deprotonated acid molecules. This same relationship holds for bases as well, with [B] substituting for [A-] as the deprotonated form, and [HB+] substituting for [HA] as the protonated form. It should be emphasized that the Henderson-Hasselbach relationship holds for a specified acid or base even if multiple acids or bases are present. Other solutions to the Henderson-Hasselbach equation over a range of pH values are displayed in the following figure (for acetic acid).
|
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics
The University of Arizona
January 6, 1999
Revised: October 2004
Contact the Development Team
http://biology.arizona.edu
All contents copyright © 1999. All rights reserved.