HIV and AIDS Problem Set
Problem 6: Protease inhibition
|
Tutorial to help answer the question Protease inhibitors prevent:
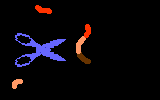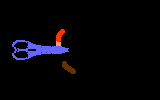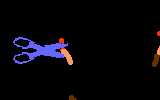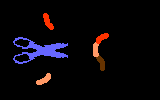
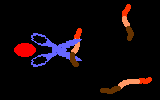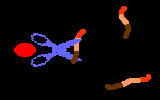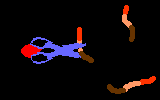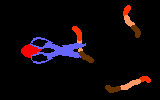
TutorialWhen a virus infects a host cell it "hijacks" the cell's protein-producing machinery, using the host to make viral proteins needed for viral replication. In HIV-infected cells, the host produces one long viral protein, or polypeptide. Protease is the enzyme that cuts this long polypeptide chain into multiple smaller proteins essential for viral reproduction.
Protease inhibitors block the action of the protease enzyme. Protease inhibitors are the second class of anti-HIV drugs currently available.
View animations of the HIV lifecycle and descriptions of drug actions,
courtesy of CellsAlive
|
The University of Arizona
Monday, April 3, 2000
Contact the Development Team
http://biology.arizona.edu
All contents copyright © 2000. All rights reserved.