The Biology Project > Biochemistry > The Chemistry of Amino Acids
Isoleucine I (Ile)
Chemical Properties:
Aliphatic
(Aliphatic R-group)Physical Properties:
Nonpolar
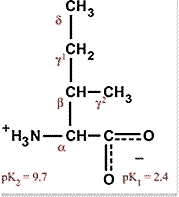
Isoleucine, an essential amino acid, is one of the three amino acids having branched hydrocarbon side chains. It is usually interchangeable with leucine and occasionally with valine in proteins.The side chains of these amino acids are not reactive and therefore not involved in any covalent chemistry in enzyme active centers.
However, these residues are critically important for ligand binding to proteins, and play central roles in protein stability. Note also that the β carbon of isoleucine is optically active, just as the β carbon of threonine. These two amino acids, isoleucine and threonine, have in common the fact that they have two chiral centers.

The Biology Project > Biochemistry > The Chemistry of Amino Acids
http://biology.arizona.edu
All contents copyright © 2003. All rights reserved.