The Biology Project > Cell Biology > Cell Membranes > Problem Set
Cell Membranes Problem Set
Problem 2: Lipids and aqueous barriers
Tutorial to help answer the question
While on a trip to the desert, a friend of yours was bitten by a rattlesnake. He nearly died from hemolysis, or breakage of many of his red blood cells. You have analyzed the snake venom and found three enzymes: phospholipase, which degrades phospholipids; neuraminidase, which removes cell surface carbohydrates; and protease which degrades proteins. Which of these enzymes do you think was responsible for his near fatal red blood cell hemolysis? Why?
A. The neuraminidase lysis the carbohydrate-rich membrane, leading to cell breakage. B. The protease would degrade transmembrane proteins leading to cell lysis. C. The phospholipase would degrade the phospholipids, the component of a membrane creating a barrier.
Tutorial
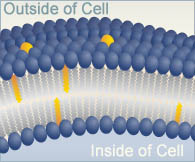
Phospholipid bilayer
The tutorial for question 1 covers this problem in detail. The phospholipid bilayer forms a barrier, preventing contents of the red blood cell from leaving the cell.
Phospholipases degrade phospholipids, and would cause hemolysis, or loss of the integrity of the red blood cell membrane leading to loss of hemoglobin from inside the cell.
The chances of being bitten by a rattlesnake are very small. Many people are bitten when they attempt to catch the snake. The treatment for a rattlesnake bite is to get the person to an emergency room that can administer antivenom, or antibodies that can neutralize protein in venom.
The Biology Project > Cell Biology > Cell Membranes > Problem Set
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics
University of Arizona
May 2002
Revised: August 2004
Contact the Development Team
http://biology.arizona.edu
All contents copyright © 2002-04. All rights reserved.