Chemistry Tutorial
Chemical bonds and attractive forces
| A molecule is two or more atoms linked by a chemical bond. Molecules can contain different types of bonds. If atoms are sharing electrons, then the bond between them is covalent. If an atom gives up an electron to another atom, then they have an ionic bond. |
|
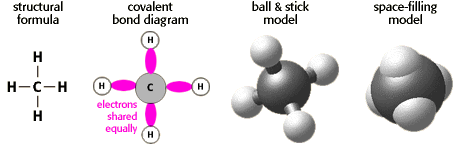
Methane has four covalent bonds between carbon (C) and hydrogen (H). The figure below shows the methane molecule in four different views.
Notice how these different views represent the atoms and their bonds differently. Electronegativity refers to the tendency for atoms to bind electrons.
Oxygen (0) with an electronegativity of 3.5 has a strong affinity. Hydrogen (H)(2.1) and carbon (C)(2.5) each have lower affinities. A bond between C and H will have nearly equal sharing of electrons.
Oxygen and hydrogen form a highly polar bond because of the much stronger affinity for electrons by O.
|
 |
Insulin is a complicated molecule called a protein. We will later consider simpler ways to consider the complicated molecules of life. |
 |
Ions are produced when atoms can obtain a stable number of electrons by giving up or gaining electrons. For example Na (sodium) can donate an electron to Cl (chlorine) generating Na+ and Cl-. The ion pair is held together by strong electrostatic attractions. |
Linus Pauling, 1946
- Chemical reactivity of molecules- tendency to break and form chemical bonds.
- Biology of molecules- size and shape of molecules, and the nature of weak interactions with other molecules.
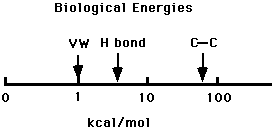
- Electrostatic bonds(ionic)-result from the electrostatic attraction between two ionized groups of opposite charge, such as carboxyl (-COO-) and amino (-NH3+). In water, these bonds are very weak.
- Hydrogen bonds-result from electrostatic attraction between an electronegative atom (O or N) and a hydrogen atom that is bonded covalently to a second electronegative atom.
- N-H ----- O=C- -O-H----- O=C-
- Van der Waals bonds-are short range attractive forces between chemical groups in contact. Caused by slight charge displacements.
- Hydrophobic attractions-cause non-polar groups such as hydrocarbon chains to associate with each other in an aqueous environment.
- Multiple weak bonds or forces can cause strong interactions
- Biological recognition results from a three dimensional structure that allows multiple weak forces between molecules
 |
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics
The University of Arizona
Revised: January 28, 2003
Contact the Development Team
http://biology.arizona.edu
All contents copyright © 1997-2003. All rights reserved.